
Total assets are the total of current assets, such as marketable securities and prepayments, and long-term assets, such as machinery and fixtures. Total liabilities are obtained by adding current liabilities and long-term liabilities. Shareholders’ equity can also be calculated by taking the company’s total assets less the total liabilities. The account demonstrates what the company did with its capital investments and profits earned during the period. To compute total liabilities for this equity formula, add the current liabilities such as accounts payable and short-term debts and long-term liabilities such as bonds payable and notes. In this formula, the equity of the shareholders is the difference between the total assets and the total liabilities.
How to calculate leverage?

Investors contribute their share of paid-in capital as stockholders, which is the basic source of total stockholders’ equity. The amount of paid-in capital from an investor is a factor in determining his/her ownership percentage. In most cases, retained earnings are the largest component of stockholders’ equity.
How Do Stock Buybacks Impact Shareholders Equity?
If it’s negative, the company has more liabilities than assets, which could put off investors who consider such businesses to be risky investments. Equity held by shareholders, however, is not the only measure of a company’s financial stability. Therefore, it should be used in conjunction with other metrics to provide a more complete view of how a business is doing.
- The remaining claims of a corporation’s owners against the company after its debts have been settled are referred to as shareholders equity.
- Total equity (book value) might be equivalent to total shareholder equity on a company’s balance sheet if you look at it from the standpoint of book value.
- Due to their reduced expenses, newer or conservatively run businesses may not need as much capital to generate free cash flow.
- Of course, when making investment decisions such as these, wise investors combine ROE alongside other metrics to get a complete picture.
- What investors generally see as a negative indicator is if ROE is declining.
- Remember, a company’s balance sheet should always balance, meaning the total assets should equal the sum of total liabilities and stockholders’ equity.
- A home equity loan is a lump sum of money that you repay over time, typically 5 to 15 years.
Everything to Run Your Business

Using the return on equity ratio, equity investors can determine the return the company made on their equity investment (ROE). In essence, a company’s net income is divided by the equity of its shareholders to calculate its return on equity. The fundamental accounting equation is the quickest and easiest way to determine shareholders’ equity. For mature companies consistently profitable, the retained earnings line item can contribute the highest percentage of shareholders’ equity. In these types of scenarios, the management team’s decision to add more to its cash reserves causes its cash balance to accumulate. If we rearrange the balance sheet equation, we’re left with the shareholders’ equity formula.
What Can Shareholder Equity Tell You?
A statement of retained profits, which summarizes the changes in retained earnings for a given time period, is also kept. In accounting for share-related transactions, a few more phrases are crucial. The number of shares authorized is the total number of shares that the corporation may issue under the articles how to calculate stockholders equity of incorporation of the business. The phrase “number of shares issued” refers to the total number of shares that the corporation has issued which may or may not be owned by outside investors. Corporations like to set a low par value because it represents their “legal capital,” which must remain invested in the company and cannot be distributed to shareholders. Another reason for setting a low par value is that when a company issues shares, it cannot sell them to investors at less than par value.
Components of Shareholders Equity
- Shareholders’ equity refers to the owners’ claim on the assets of a company after debts have been settled.
- For example, if a company reports a return on equity of 12% for several years, it is a good indication that it can continue to reinvest and grow 12% into the future.
- At that time, XYZ Ltd. had $7 billion in total shareholders’ equity (or assets minus liabilities).
- This reverse capital exchange between a company and its stockholders is known as share buybacks.
- Companies may return a portion of stockholders’ equity back to stockholders when unable to adequately allocate equity capital in ways that produce desired profits.
- When considering ROE as a measurement of financial health, investors should look at how the company is leveraged.
Companies can artificially boost ROE by increasing debt, which reduces shareholders’ equity. This is why investors must also assess the company’s financial leverage to ensure the high ROE is sustainable. Retail Accounting To calculate stockholders’ equity, you can use one of two accounting equations. Businesses have assets (resources owned or operated by the company that add to its economic value) and liabilities (debts or obligations that detract from its economic value). Shareholders’ equity indicates the money that would belong to the company’s owners and shareholders after it sold all of its assets and took care of all its liabilities. If it’s in the black, then the company’s assets are more than its liabilities.
- You’ll need to multiply this by 0.8 and subtract what you owe on the mortgage to see how much you can borrow.
- A dividend payable account is used by the corporation to record the obligation to pay a dividend once it is declared by the board.
- Positive shareholder equity means the company has enough assets to cover its liabilities.
- Using our original example, your home is worth $500,000 and you have $300,000 left on your mortgage.
- But an important distinction is that the decline in equity value occurs due to the “book value of equity”, rather than the market value.
- Return on Equity (ROE) speaks to how effectively your company generates profit from its shareholders’ investment.
How to calculate net leverage ratio?
A reverse mortgage is a type of home loan that allows you to receive your home’s equity in the form of a payment each month. You can usually get a reverse mortgage once you’ve paid off – or are close to paying off – your mortgage, but you need to be 62 years of age. As a result, you’re able to tap into your home equity without a HELOC or home equity loan. If you have a conventional mortgage and paid a down payment below 20% then you’re likely paying PMI. If you’ve reached the point where you no longer pay PMI, usually at 20% equity, it won’t affect your ability to get a home equity loan or HELOC.

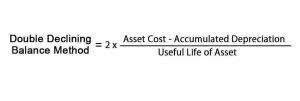
The calculation includes information from the company’s balance sheet; it can be difficult to pinpoint the accuracy of depreciation and other factors. In addition, a company’s assets and liabilities can change at any time because of unforeseen circumstances. Shareholders’ equity includes preferred stock, common stock, retained earnings, and trial balance accumulated other comprehensive income.

Leave a Reply